Awe-Inspiring Examples Of Tips About Depreciation Expense Financial Statement 3 Model Excel Template

Understanding the basics of depreciation expense
Depreciation expense financial statement. If the asset is used for production, the expense is listed in the operating expenses area of. Periodic depreciation expense = beginning value of asset * factor / useful life. It reduces net income but does not affect cash flow.
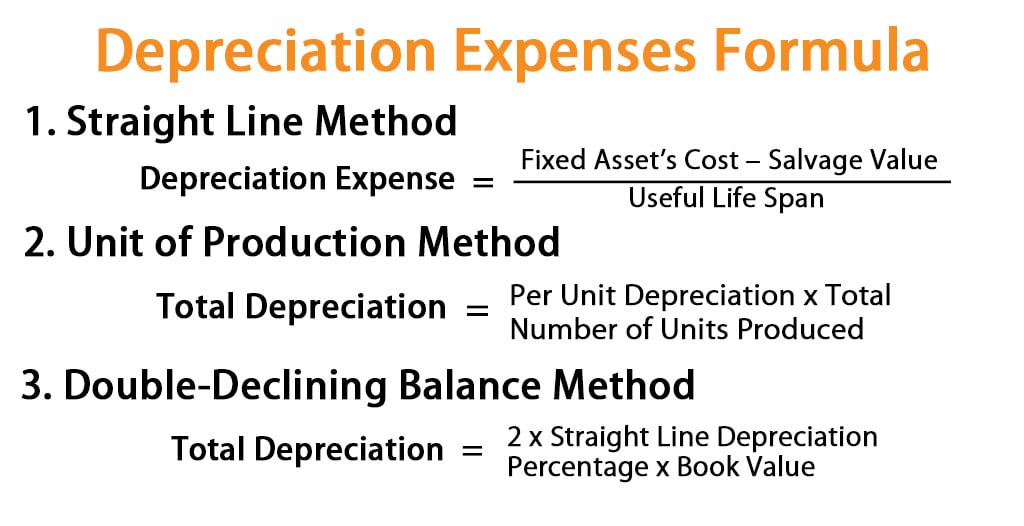
Depreciation may be defined as the decrease in the asset’s value due to wear and tear over time. Depreciation expense is a fundamental concept in finance and accounting that. The depreciation expense will be calculated on the following formula:
Depreciation also appears on the income statement as a depreciation expense. The asset cost minus the salvage value equals the overall depreciation. Welcome to the world of finance, where numbers and reports play a crucial role in understanding the.
Accumulated depreciation appears in a contra asset account on the. Depreciation method you can use two main approaches to. Calculating depreciation using the declining balance method.
The formula of depreciation expense is used to find how much asset value can be deducted as an expense through the income statement. Example of depreciation expense to illustrate depreciation expense, assum. The asset’s net book value falls as accumulated depreciation rises.
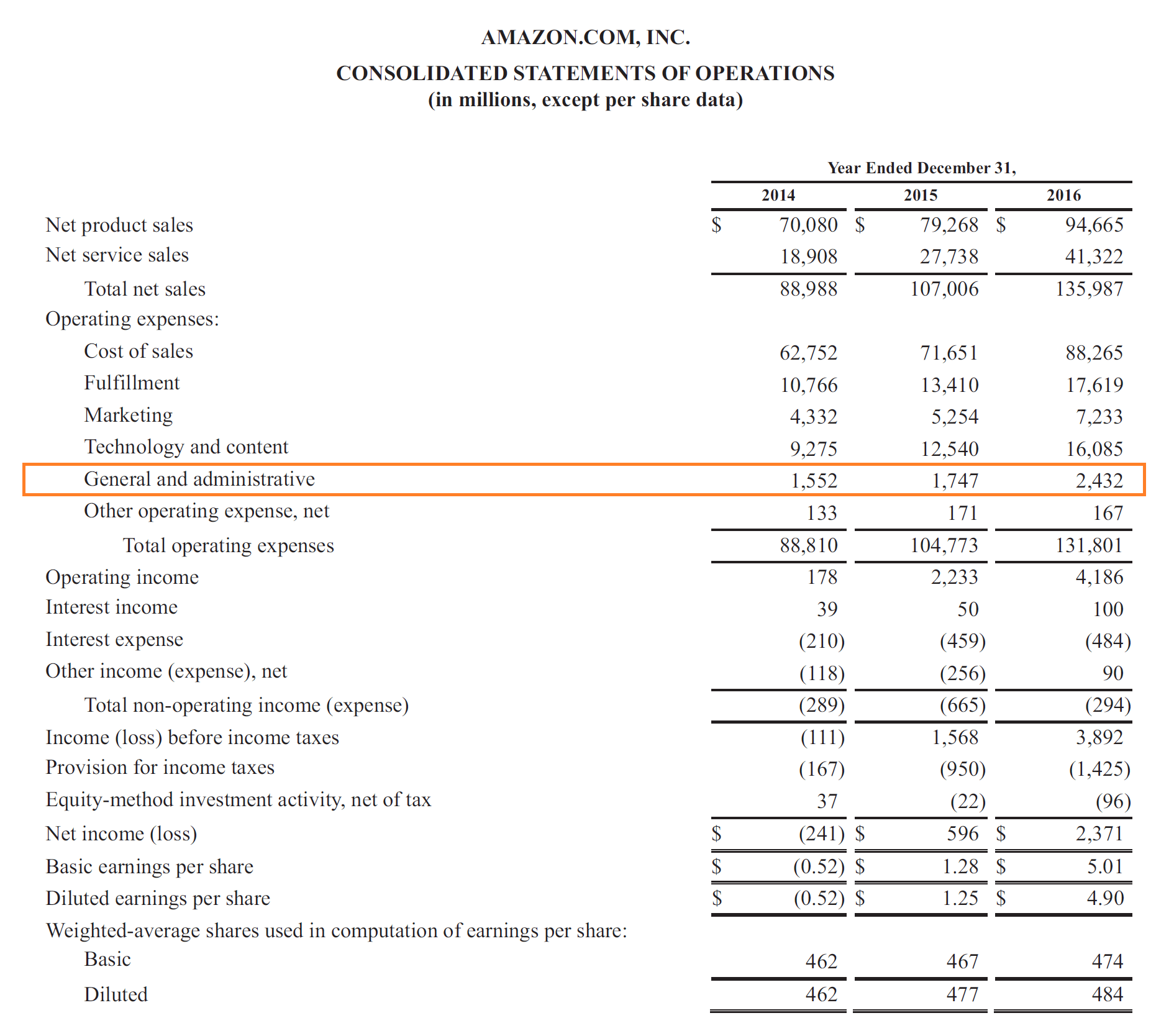
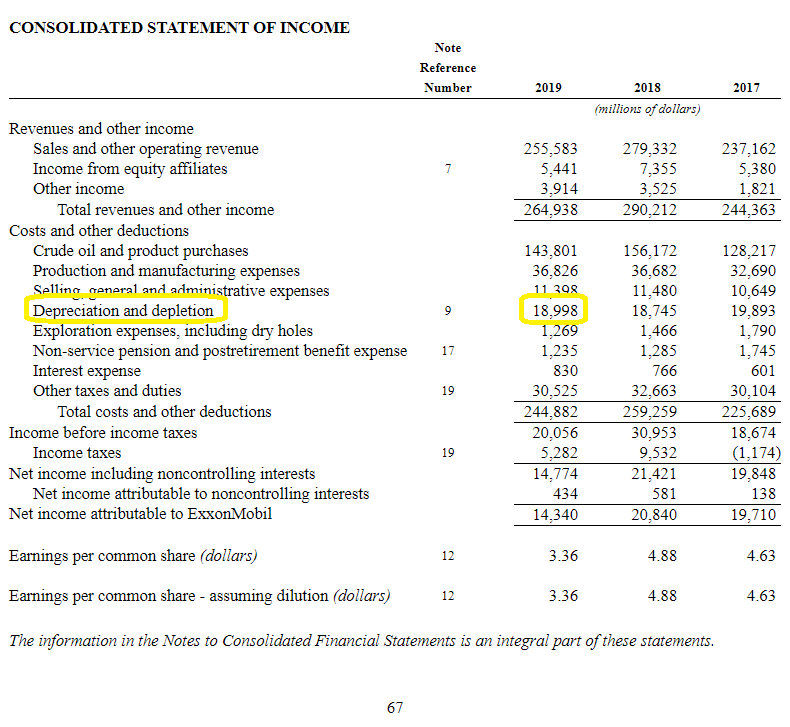
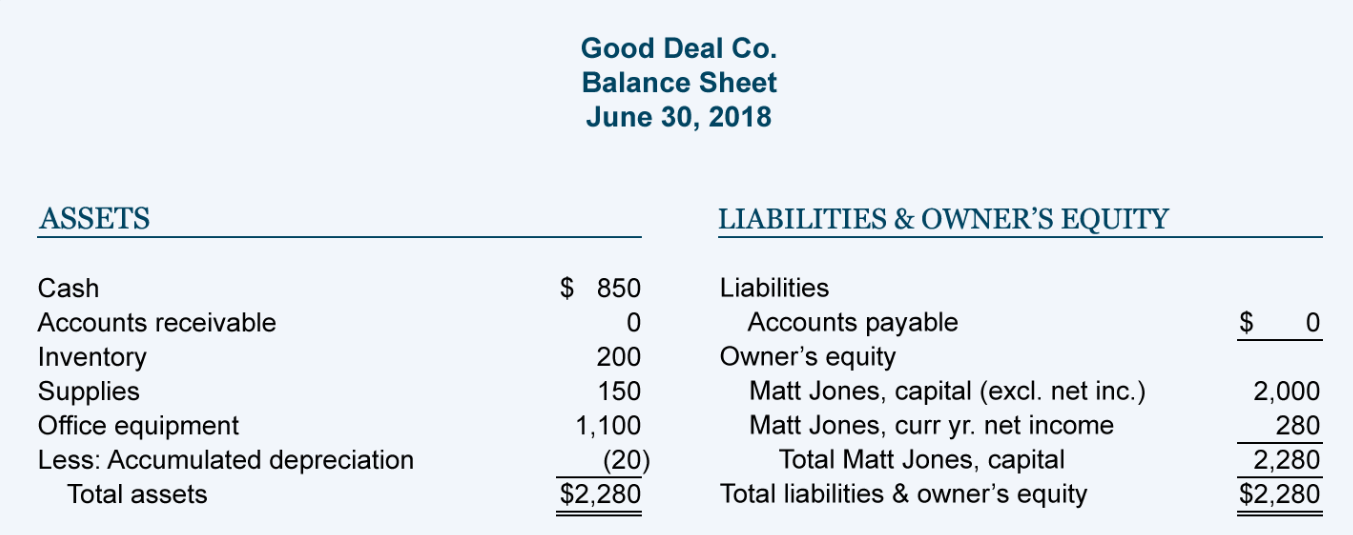
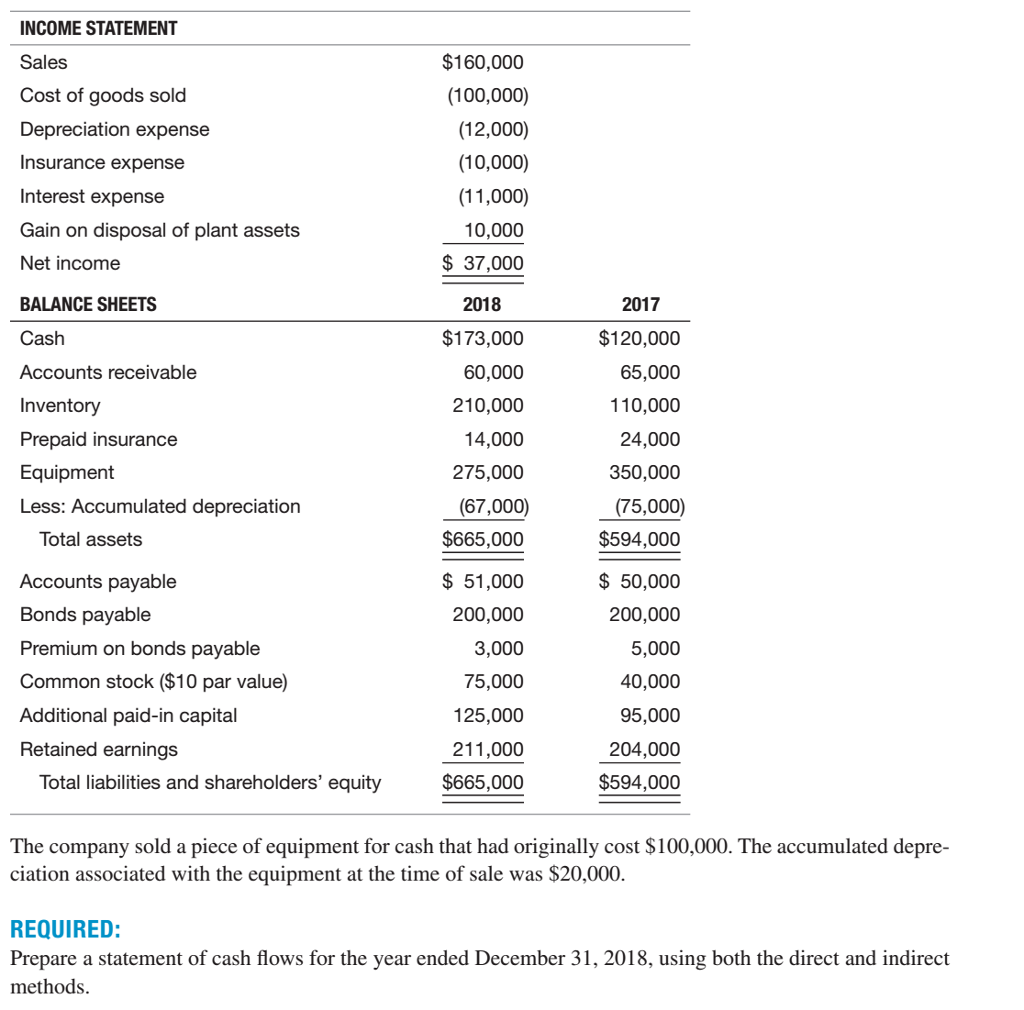
Depreciation expense is reported on which of the following financial statements? As you can see, from a tax perspective the tax payable would be $30 higher than the tax calculated on the business' net accounting profit. Depreciation expense on the income statement is the product of determining depreciation based on the schedule set up by.
How is depreciation expense reported in the financial statements introduction. Depreciation represents how much of the asset's value has been used up in. Physical assets, such as machines, equipment, or vehicles, degrade over time and reduce in value incrementally.
$25,000 x 30% = $7,500. Depreciation is a type of expense that is used to reduce the carrying value of an asset. This expense is subtracted from the company's revenue to calculate its operating income or earnings before interest and taxes (ebit).
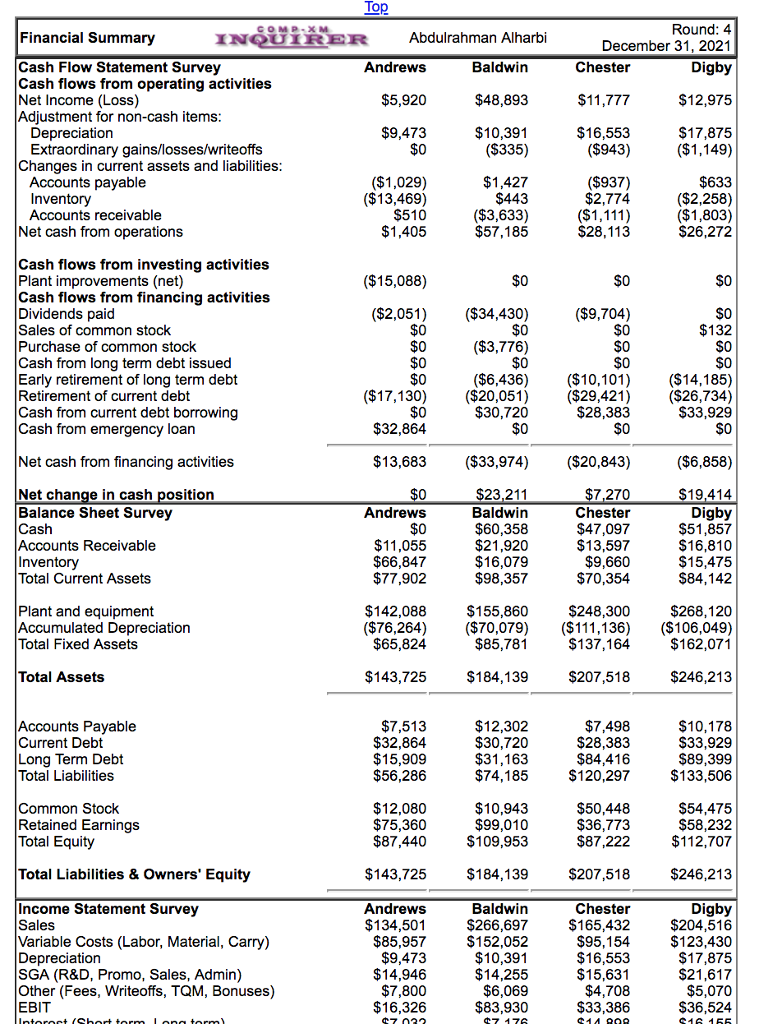
The depreciation expense amount changes every year because the factor is multiplied with the previous period’s net book value of the asset, decreasing. Depreciation expense is reported on the income statement as any other normal business expense. The amount of depreciation expense reflects the wear and tear or obsolescence of a company’s assets over time.
The depreciation expense is indicated under operating expenses for a given period. Depreciation expense allows accounting to purchase that asset and account for the impact over a longer period. Many companies list the expense on their income statement as an operating cost for the business.







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Walmart202010KIncomestatement-365d4a49671b4579a2e102762ada8029.jpg)

