Inspirating Info About Contingent Liabilities In Balance Sheet Define Comprehensive Income

In 2022, the level of government guarantees was.
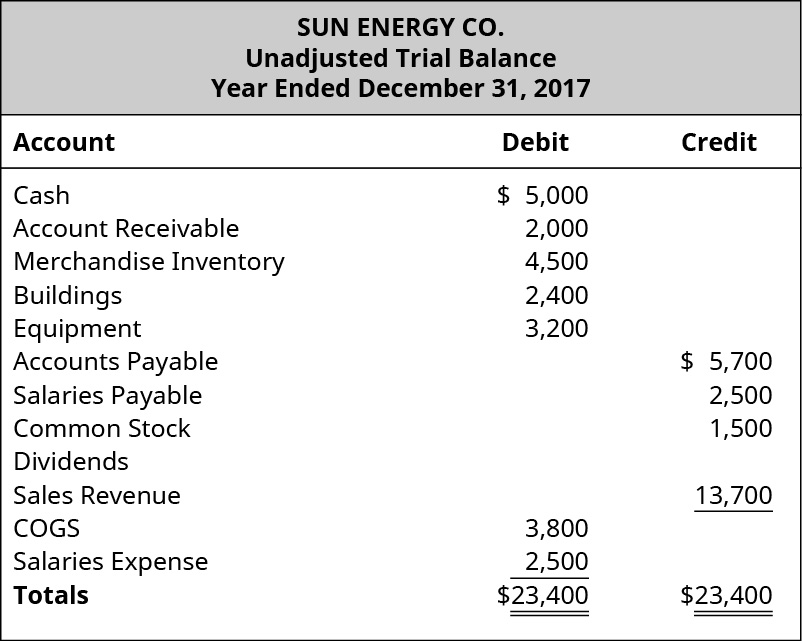
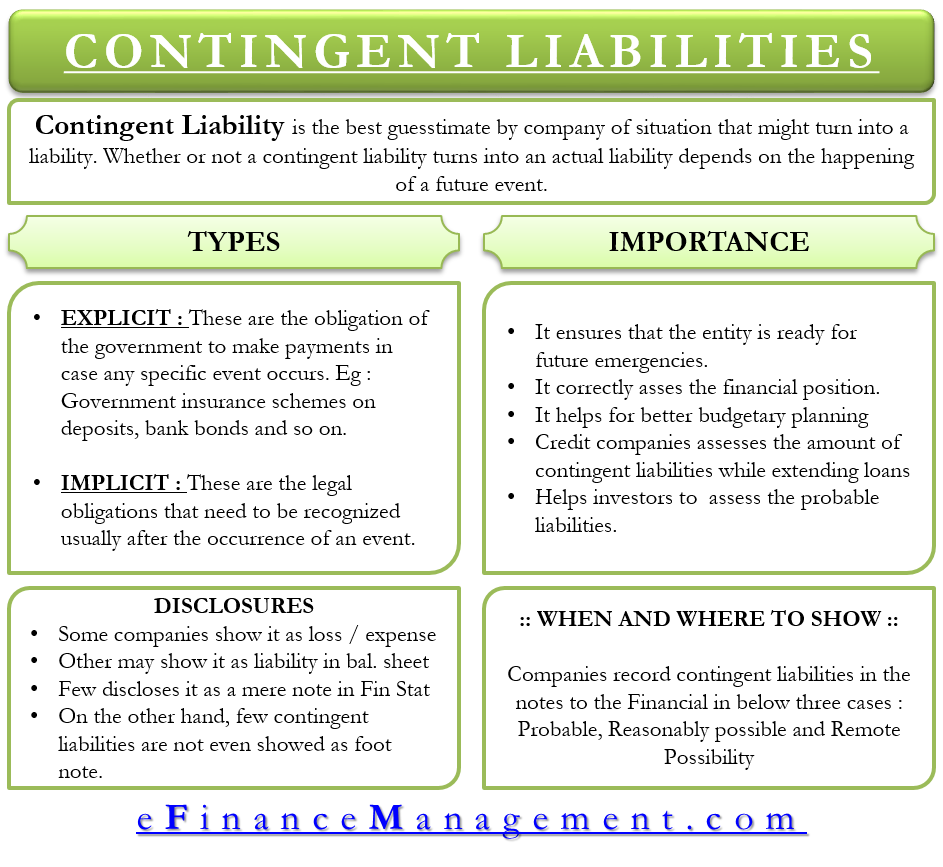
Contingent liabilities in balance sheet. Ias 37 outlines the accounting for provisions (liabilities of uncertain timing or amount), together with contingent assets (possible assets) and contingent liabilities (possible obligations and present obligations that are not probable or not reliably measurable). The relevance of a contingent liability depends on the probability of the contingency becoming an actual liability, its timing, and the accuracy with which the amount associated with it can be estimated. Contingent liabilities are potential liabilities that may or may not arise depending on the outcome of a future event.
Ias® 37, provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets appears to be less popular than other standards because, usually, answers to financial reporting (fr) questions require a balanced discussion of whether criteria are met, as opposed to calculating numbers. Contingent liabilities are recorded if the contingency is likely and the amount. In simple words, contingent liabilities are those obligations that will arise in future due to certain events that took place in the past or will be taking place in future.
Recording a contingent liability a potential or contingent liability that is both probable and the amount can be estimated is recorded as 1) an expense or loss on the income statement, and 2) a liability on the balance sheet. Or an assessment that contingent liabilities. A contingent liability will only be recorded in the balance sheet when the probability of its occurrence is certain, and the extent of such liability can be determined.
Or, if you prefer to look at it in equity terms: So, according to the definition, contingent liabilities are those liabilities that may or may not be incurred by a business depending on the outcome of a future event. Ias 37 defines and specifies the accounting for and disclosure of provisions, contingent liabilities, and contingent assets.
Contingent liabilities in balance sheet or footnotes. The objective of ias 37 is to ensure that appropriate recognition criteria and measurement bases are applied to provisions, contingent liabilities and contingent assets and that sufficient information is disclosed in the notes to the financial statements to enable users to understand their nature, timing and amount. These liabilities are also recorded in the accounting books if the amount of the liability can be estimated.
These liabilities are posted in the balance sheet. Whether vested or contingent and whether personal or assignable) in real or personal property of any description (including money), and includes securities, choses in action and documents. A provision is a liability of uncertain timing or amount.
Contingent liabilities are liabilities that depend on the outcome of an uncertain event. That standard replaced parts of ias 10 contingencies and events occurring after the balance sheet date that was issued in 1978 and that dealt with contingencies. The liability may be a legal.
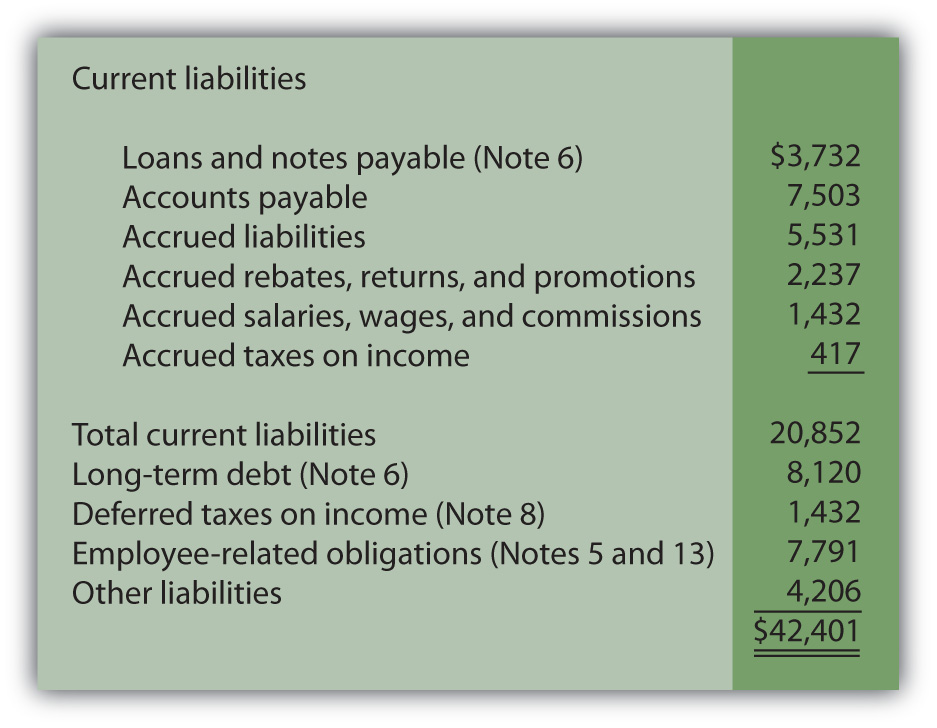
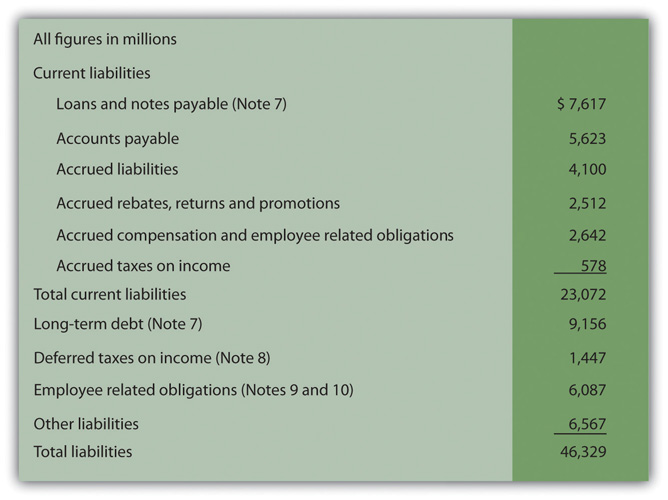
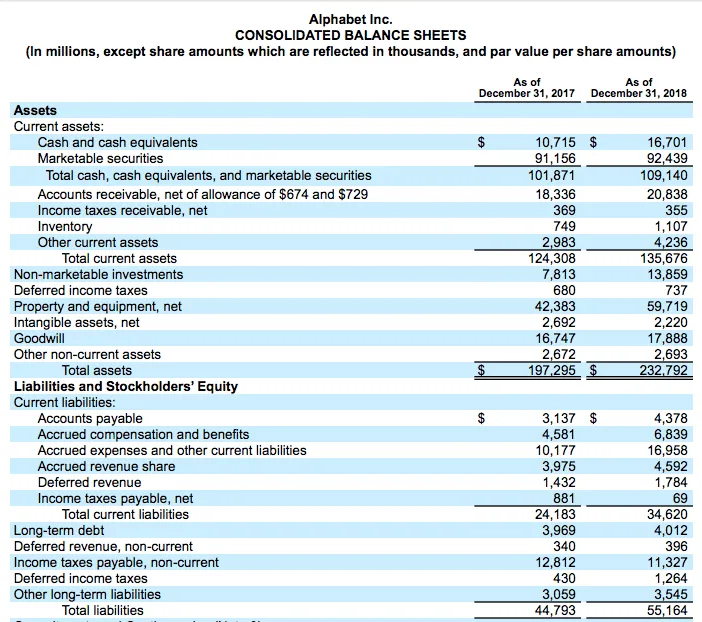
The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company’s financial condition — its assets, liabilities, and equity at a particular time. If a contingent liability carries a 50% or higher risk of being realised, it is posted in the profit & loss account as well as the balance sheet. Like many other companies, contingent liabilities are carried on google’s balance sheet, report expenses related to these contingencies on its income statement, and note disclosures are provided to explain its contingent liability treatments.
This liability is not yet an actual, confirmed obligation. These liabilities are recorded in the balance sheet. Contingent liabilities and contingent assets, which had originally been issued by the international accounting standards committee in september 1998.
Probable contingency a probable contingency describes a scenario wherein the risk of liability occurring is greater than 50% (ifrs) or 80% (gaap). There are numerous examples of contingent liabilities. Disclosing a contingent liability a loss contingency which is possible.

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/contingentliability-Final-84e09f386f114ab0b786c4a2ad5bad18.jpg)